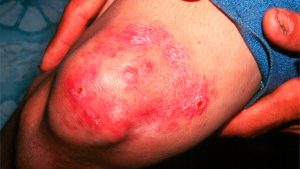
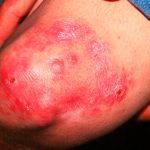
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection that occurs in the skin and subcutaneous tissues. It is very frequent and without the proper treatment in time it can become a potentially severe disease. The Cellulitis manifests in any part of the body, although it is more common to find it in the lower part of legs or damaged skin. Anyone can develop this condition no matter sex or age, though there is a higher risk in people who smoke, have diabetes or circulation problems.
This skin disease exposes as a swollen and red area that also feels hot. After appearing in an area, it can easily spread to other regions of the body or face. The Cellulitis affects the outer surface of skin and tissues beneath it and eventually spreads to lymph nodes and the bloodstream. Its propagation can quickly put lives at risk. If there are Cellulitis symptoms, it is important to seek medical help immediately.
The most common bacteria that develop Cellulitis are Staphylococcus aureus (golden staphylococcus) and group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus. They enter damaged or healthy skin, so it is necessary to use antibiotics to treat the bacterial infection. Previously, when the use of antibiotics had not been developed, Cellulitis involved death; therefore it could be a fatal condition. Since the invention of penicillin, a patient with cellulitis can recover in just one week.
Regularly, with a seven to ten days antibiotics treatment, Cellulitis disappears. But, if the infection is too strong, the antibiotics treatment may be prolonged, especially if there are other chronic conditions or a debilitated immune system.
Cellulitis symptoms
It is crucial to recognize Cellulitis symptoms and act as quickly as possible since this condition has the fundamental characteristic of fast spread in the body. Among the primary symptoms they are:
- Fever due to infection.
- Pain and hypersensitivity where cellulitis takes place.
- Inflammation and redness of the affected skin, also making the area larger as the infection begins to spread.
- The affected area becomes hot.
- In the first 24 hours, the skin lesion appears with sudden eruptions, as well as it rapidly grows.
- The skin looks tense, bright and stretched.
- The joints become stiff due to inflammation of tissue over the joint.
- Nausea and vomiting.
When the infection is latent in the human body, chills and shivering, fatigue, malaise, myalgia, pains and sweating appear too.
What causes Cellulitis?
Cellulitis takes place in the body when bacteria, which mostly are streptococci and staphylococci, enter the skin through a crack or fissure. It can appear anywhere on the body, but the most common area is the legs, as well as specific points where are cuts, puncture wounds, ulcers, athlete’s foot, dermatitis or recent surgery.
Others cellulitis causes may be insects or spiders bites that transmit the bacteria that later lead to infection. In healthy skin, inhabit many types of bacteria that can enter the body through a skin break, dry areas, scaly or swollen skin. Besides, some risks factors increase the chances of suffering from Cellulitis:
- Peripheral vascular disease history or having vascular disease or diabetes increases the chances of developing Cellulitis.
- Ulcers caused by other diseases such as diabetes.
- People who have had Cellulitis before, especially on legs, may be more likely to have it again.
- Weakened immune system. Suffering from any disease that weakens the immune system, such as diabetes, leukemia and HIV / AIDS, make more susceptible developing infection. Also, using corticosteroid medications or related drugs that suppress defenses of the immune system.
- Skin lesions. Burns, abrasions or cuts; ruptures or skin peeling between fingers, skin wounds, wounds from recent surgeries; any of them represents an entry for bacteria.
- Bites from insects, other animals or people.
- Skin diseases. Other skin conditions such as eczema, athlete’s foot, chicken pox, shingles, psoriasis or acne, can lead the bacteria to enter the body.
- Chronic swelling of arms or legs (lymphedema). The swollen tissue can crack and leave the skin vulnerable to bacterial infection.
- Skin inlays of objects or materials such as metal or glass.
- Intravenous drug use. People who inject illegal drugs have a higher risk of Cellulitis.
- Being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing Cellulitis and in addition to repeating the condition in future.
Cellulitis treatment
After having the infection latent, the treatment to mitigate it is taking oral antibiotics with analgesics for those who start the disease. For people who suffer from a severe condition of Cellulitis and are seriously ill, it is best to administer antibiotics intravenously to control and prevent further spread of the infection. This treatment must be applied in a hospital or at home by a local doctor or nurse. Always raising the infected area higher than the level of the heart to reduce inflammation and accelerate the sanitation process.
If the patient has a high fever, uncontrolled blood pressure, nausea and vomiting, it is best to stay at the hospital until the symptoms disappear or are in control. Nor can go home if the antibiotics do not work or worsen Cellulitis conditions. Neither if the patient has a deficit in the immune system or infection around eyes.
If the infection gets better, the treatment can pass to oral antibiotics that can be taken at home for up to 10 days. Regularly the improvements in patient begin to be visualized after two or three days of antibiotic treatment. The cases are rare, but the infection may get worse by spreading to deeper tissues in which cases, in addition to using broad-spectrum antibiotics, the treatment requires surgery.
Part of the treatment is also full rest until the symptoms disappear completely. And to prevent the infection from spreading, the patient has to wash hands continuously, clean the wound with antiseptic solution and cover it with a gauze dressing.
Cellulitis Complications
The bacteria that lead to Cellulitis can spread rapidly to reach lymph nodes and bloodstream. If recurrent episodes of Cellulitis occur, it can affect the lymphatic drainage system, causing chronic swelling and becoming an extreme emergency.
In general, if Cellulitis is not treated on time or the treatment used does not work to reduce the symptoms, and the infection spreads, it may lead to other health complications:
- Lymphangitis, inflammation of the lymphatic vessels.
- Osteomyelitis, bone system infection.
- Sepsis, blood infection
- Endocarditis, inflammation of the heart.
- Meningitis, infection of the membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord.
- Gangrene, the death of tissues.