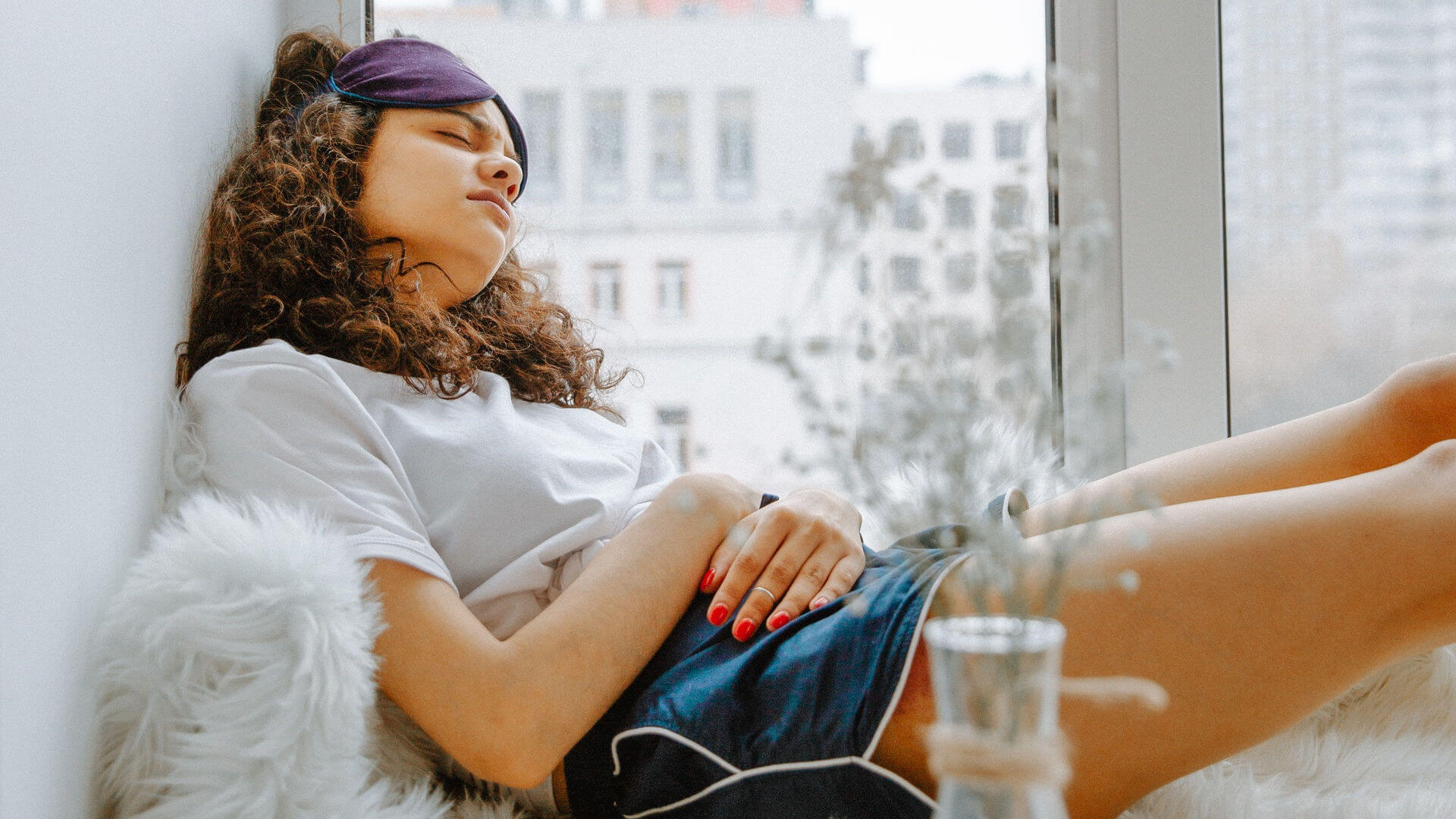
For centuries, heat and cold therapies have been used to manage muscular and body pain. Under the right circumstances, and with proper application, the results are far better compared with modern-day medicine. With prolonged use, modern medications have an array of side effects that can lead to health issues. For severe cases, modern medicine has invasive and addictive therapies for managing pain which often leave scars on the body.
Cold and heat therapies are not invasive and are non-addictive – this makes them a convenient and reliable alternative to medicines. However, professional guidance is necessary to minimize the risks of incorrect application. In broad terms, heat application revolves around vasodilation that increases blood flow to muscles and organs. Alternatively, cold therapies produce vasoconstriction that slows blood circulation.
Where to apply heat therapy?
Heat therapies are used to create vasodilation to increase blood flow to tissues and relieve pain and muscle stiffness. Vasodilation promotes blood flow to muscles and organs which increases the flow of oxygen, thus delivering more nutrients and removing cell waste. Additionally, the heat itself relaxes muscles and reduces muscle spasms. Heat therapy is effective for relieving muscle pain and stiffness by applying directly to the affected area. Heat therapy also provides fast and effective relief for lower-back pain or post-exercise pain. These days, you can find many heat therapy products that produce similar results. There are electronic devices that generate heat and can be applied directly to the affected area for quick relief.
Traditionally, water bags were filled with warm or hot water and used to relieve pain and muscle spasms. Today, you can buy disposable heat packs that are ideal for one-time use. It is advisable to wrap heat packs in a towel or cloth to prevent burns.
How to use Cold therapy?
Cold therapy is commonly used to relieve swelling in the body. Lower blood circulation reduces inflammation, pain and muscle spasms. Cold therapy does not
have to be applied as frequently as heat therapies. In most cases, cold therapy lasts for about 15 minutes. You can buy cold packs from most drug stores, and at many supermarkets. Cold therapies are ideal for reducing swelling and inflammation of muscles. Application is similar to heat therapy and requires direct application over the affected area. It is recommended to use a towel or cloth with a cold pack to avoid discomfort and nerve damage. If you are using commercial cold packs, discard them if they are punctured because they contain chemicals that can cause
skin irritation/burns.
The right combination of heat and cold therapies are effective for reducing muscle pain and inflammation. However, it is necessary to use heat and cold therapies with caution and get professional guidance in order to avoid unnecessary damage to the skin and nerves.